Introduction of Dissolved oxygen meter

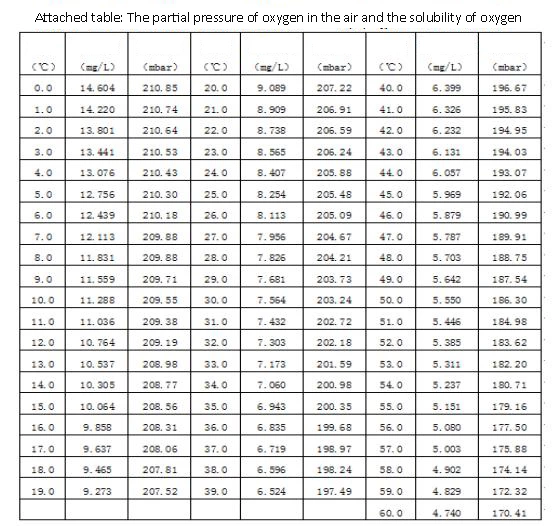
Dissolved oxygen refers to the amount of oxygen dissolved in water, usually recorded as DO, expressed in milligrams of oxygen per liter of water (in mg/L or ppm). Some organic compounds are biodegraded under the action of aerobic bacteria, which consumes the dissolved oxygen in the water, and the dissolved oxygen cannot be replenished in time. The anaerobic bacteria in the water body will multiply quickly, and the organic matter will turn the water body black due to corruption. smell. The amount of dissolved oxygen in the water is an indicator to measure the self-purification ability of the water body. The dissolved oxygen in the water is consumed, and it takes a short time to restore to the initial state, indicating that the water body has a strong self-purification ability, or that the water body pollution is not serious. Otherwise, it means that the water body is seriously polluted, the self-purification ability is weak, or even the self-purification ability is lost. It is closely related to the partial pressure of oxygen in the air, atmospheric pressure, water temperature and water quality.
1.Aquaculture: to ensure the respiratory demand of aquatic products, real-time monitoring of oxygen content, automatic alarm, automatic oxygenation and other functions

2.Water quality monitoring of natural waters: Detect the pollution degree and self-purification ability of waters, and prevent biological pollution such as eutrophication of water bodies.
3. Sewage treatment, control indicators: anaerobic tank, aerobic tank, aeration tank and other indicators are used to control the water treatment effect.
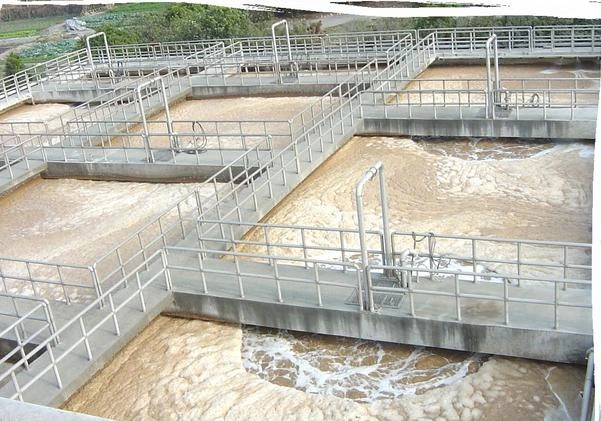

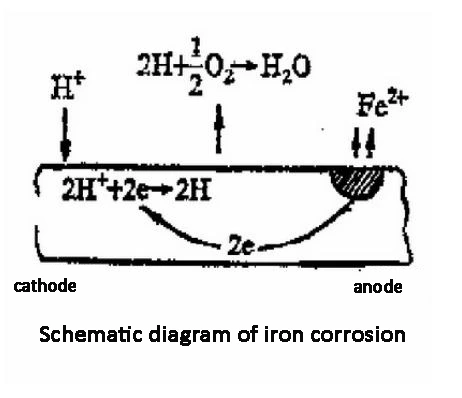
4. Control the corrosion of metal materials in industrial water supply pipelines: Generally, sensors with ppb (ug/L) range are used to control the pipeline to achieve zero oxygen to prevent rust. It is often used in power plants and boiler equipment.
At present, the most common dissolved oxygen meter on the market has two measurement principles: membrane method and fluorescence method. So what is the difference between the two?
1. Membrane method (also known as polarography method, constant pressure method)
The membrane method uses electrochemical principles. A semi-permeable membrane is used to separate the platinum cathode, silver anode, and electrolyte from the outside. Normally, the cathode is almost in direct contact with this film. Oxygen diffuses through the membrane at a ratio proportional to its partial pressure. The greater the oxygen partial pressure, the more oxygen will pass through the membrane. When dissolved oxygen continuously penetrates the membrane and penetrates into the cavity, it is reduced on the cathode to generate a current. This current is directly proportional to the dissolved oxygen concentration. The meter part undergoes amplifying processing to convert the measured current into a concentration unit.

2. Fluorescence
The fluorescent probe has a built-in light source that emits blue light and illuminates the fluorescent layer. The fluorescent substance emits red light after being excited. Since oxygen molecules can take away energy (quenching effect), the time and intensity of the excited red light are related to the oxygen molecules. The concentration is inversely proportional. By measuring the phase difference between the excited red light and the reference light, and comparing it with the internal calibration value, the concentration of oxygen molecules can be calculated. No oxygen is consumed during the measurement, the data is stable, the performance is reliable, and there is no interference.
Let's analyze it for everyone from the use:
1. When using polarographic electrodes, warm up for at least 15-30 minutes before calibration or measurement.
2. Due to the consumption of oxygen by the electrode, the concentration of oxygen on the surface of the probe will instantly decrease, so it is important to stir the solution during measurement! In other words, because the oxygen content is measured by consuming oxygen, there is a systematic error.
3. Due to the progress of the electrochemical reaction, the electrolyte concentration is constantly being consumed, so it is necessary to add electrolyte regularly to ensure the concentration. In order to ensure that there are no bubbles in the electrolyte of the membrane, it is required to remove all the liquid chambers when installing the membrane head air.
4. After each electrolyte is added, a new cycle of calibration operation (usually zero point calibration in oxygen-free water and slope calibration in air) is required, and then even if the instrument with automatic temperature compensation is used, it must be close to It is better to calibrate the electrode at the temperature of the sample solution.
5. No bubbles should be left on the surface of the semi-permeable membrane during the measurement process, otherwise it will read the bubbles as an oxygen-saturated sample. It is not recommended to use it in an aeration tank.
6. Due to process reasons, the membrane head is relatively thin, especially easy to pierce in a certain corrosive medium, and has a short life. It is a consumable item. If the membrane is damaged, it must be replaced.
To sum up, the membrane method is that the accuracy error is prone to deviation, the maintenance period is short, and the operation is more troublesome!
What about the fluorescence method? Due to the physical principle, oxygen is only used as a catalyst during the measurement process, so the measurement process is basically free from external interference! High-precision, maintenance-free, and better-quality probes are basically left unattended for 1-2 years after installation. Does the fluorescence method really have no shortcomings? Of course there is!






