SUP-ST500 Temperature transmitter programmable
Characteristics
Input signal: Resistance temperature detector (RTD), thermocouple (TC), and linear resistance.
Output: 4-20mA
Power supply: DC12-40V
Response time: Reach to 90% of the final value for 1s
Input signal: Resistance temperature detector (RTD), thermocouple (TC), and linear resistance.
Output: 4-20mA
Power supply: DC12-40V
Response time: Reach to 90% of the final value for 1s
| Input | |
| Input signal | Resistance temperature detector (RTD), thermocouple (TC), and linear resistance. |
| Cold-junction compensation temperature scope | -20~60℃ |
| Output | |
| Output signal | 4-20mA |
| Load resistance | RL≤(U-10)/0.021 |
| Output current of upper and lower limit overflow alarm | IH=21 mA, IL=3.8 mA |
| Power supply | |
| Power supply | (12-40)VDC |
| Other parameters | |
| Response time | Reach to 90% of the final value for 1s |
| Used environmental temperature | -40~80℃ |
| Storage temperature | -40~100℃ |
| Vibration resistance | 4g/2~150Hz |
| Electromagnetic compatibility | Conform to GB/T18268 industrial equipment application requirements(IEC 61326-1) |
Temperature transmitters are widely used in various industries for temperature measurement and control applications. They are highly accurate, reliable, and offer several advantages over other temperature measuring instruments. Some of the key features and advantages of temperature transmitters include:
Some specific applications of temperature transmitters include:
| Model | Type | Measurement scope | Minimum measurement scope | Accuracy |
| Resistance temperature detector (RTD) | Pt100 | -200~850℃ | 20℃ | ±0.2%/±0.4℃ |
| Cu50 | -50~150℃ | 20℃ | ±1.0%/±1.0℃ | |
| Thermocouple (TC) | B | 400~1820℃ | 500℃ | ±0.1%/±1.5℃ |
| E | -100~1000℃ | 50℃ | ±0.1%/±0.5℃ | |
| J | -100~1200℃ | 50℃ | ±0.1%/±0.5℃ | |
| K | -180~1372℃ | 50℃ | ±0.1%/±0.5℃ | |
| N | -180~1300℃ | 50℃ | ±0.1%/±0.5℃ | |
| R | -50~1768℃ | 500℃ | ±0.1%/±1.5℃ | |
| S | -50~1768℃ | 500℃ | ±0.1%/±1.5℃ | |
| T | -200~400℃ | 50℃ | ±0.1%/±0.5℃ | |
| Wre3-25 | 0~2315℃ | 500℃ | ±0.1%/±1.5℃ | |
| Wre5-26 | 0~2310℃ | 500℃ | ±0.1%/±1.5℃ |
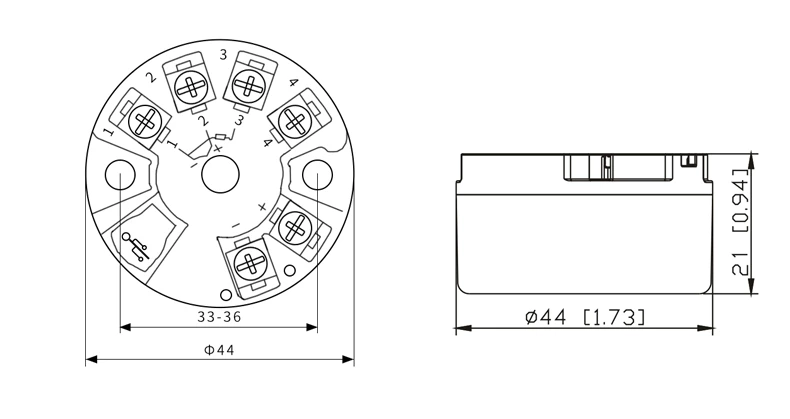
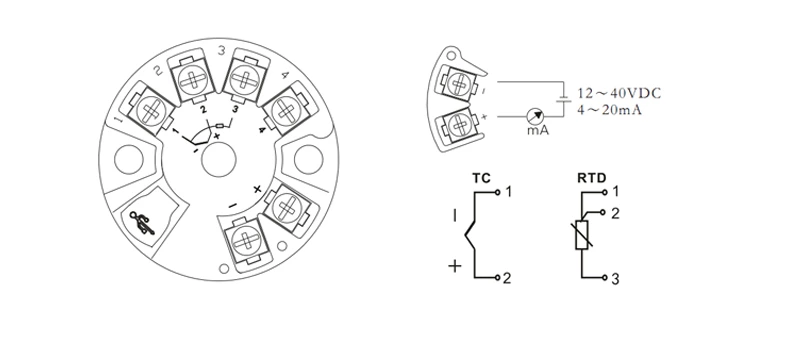
Note: no 24V power supply is required when using the V8 serial port programming line

SUP-ST500 temperature transmitter supports input signal adjustment. If you need to adjust the input signal, please let us know and we will give you software.
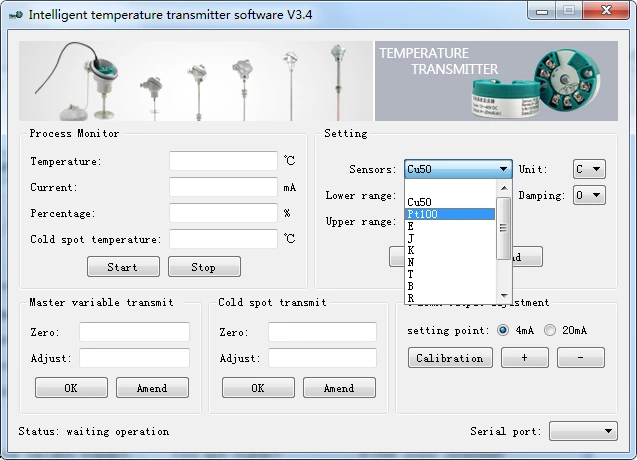
With the software, you can adjust the temperature type, such as PT100, Cu50, R, T, K etc.; input temperature range.
We use cookies to collect information about how you use this site. We use this information to make the website work as well as possible and improve our services.